What Is Cardiac Rehabilitation
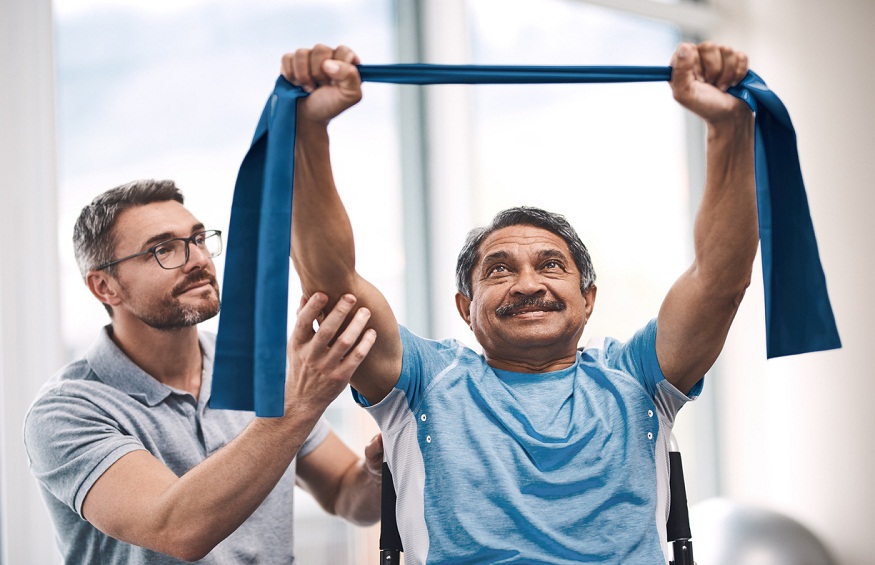

Shot of a senior man exercising with a resistance band during a rehabilitation session with his physiotherapist
A personalized clinical program of exercise and education in cardiac rehabilitation also called cardiac rehab. The program is meant to help you maintain your health and recover from a heart attack, other types of heart disease, or heart disease recovery surgery.
To minimize the risk of heart failure, cardiac rehabilitation also requires exercise preparation, emotional support and information about lifestyle improvements, such as following a heart-healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight and quitting smoking.
The type of physiotherapy aims of cardiac rehabilitation includes the creation of a plan to help you recover strength, avoid the deterioration of your condition, minimize the risk of potential heart attacks, and improve your health and quality of life.
Research has found that cardiac rehabilitation services will reduce your risk of heart attack death and decrease the risk of heart attacks in the future. Cardiac rehabilitation programs are recommended by the American
Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology.
Why it’s done
For people with several types of heart disease, cardiac rehabilitation is a choice. In particular, if your medical background includes: you may benefit from cardiac rehabilitation:
- Cardiac arrest
- Infection of the coronary arteries
- Heart failure
- Disease in the peripheral arteries
- Pain in the chest (angina)
- cardiomyopathy
- Certain congenital heart diseases
- Surgery for coronary artery bypass
- Stents and angioplasty
- Heart transplant or lung transplant
- Repair or Removal of Heart Valves
- Hypertension of the lungs
Risks
For someone who has had heart failure, cardiac rehabilitation is not suitable. To ensure that you are ready to start a cardiac recovery program, the health care provider will assess your health, including evaluating your medical history, conducting a physical examination and performing tests.
Sometimes when exercising as part of cardiac rehabilitation, some
individuals experience injuries, such as strained muscles or sprains.
To minimize this risk, the health care team will closely observe you as you exercise and teach you how to prevent injury when you exercise on your own. A slight risk of cardiovascular complications is also present.
How you prepare
Ask your doctor about joining a cardiac recovery program if you have had a heart attack, heart surgery or another heart injury. Insurance and Medicare might also cover the costs of cardiac rehabilitation in Singapore. To see if your cardiac recovery will be covered, check with your insurance provider.
Your recovery team will collaborate with you to set expectations and develop a schedule that addresses your needs for your cardiac rehabilitation program. A case manager can monitor your treatment in some situations.
If you are still in the hospital or more likely, as an outpatient, cardiac recovery will begin. A home-based program may work for some people,
particularly at certain times, such as a pandemic.
During cardiac rehabilitation
Generally, the first phases of most cardiac recovery services last about three months, but some individuals will continue the program longer. Some individuals may be able to do an intense program for several hours a day in special cases that will last one to two weeks.
You will potentially work with a team of health care practitioners during cardiac recovery, likely including cardiologists, nurse educators, nutrition specialists, fitness specialists, specialists in mental health, and physical and occupational therapists.

 The Hidden Impact of Micro-Decisions: How Small Choices Shape Big Outcomes with insights from Joe Kiani, Masimo founder
The Hidden Impact of Micro-Decisions: How Small Choices Shape Big Outcomes with insights from Joe Kiani, Masimo founder  NATURAL AND MINDFUL WAYS TO MANAGE NICOTINE CRAVINGS
NATURAL AND MINDFUL WAYS TO MANAGE NICOTINE CRAVINGS  How Mind-Body Health Fits into Chronic Care
How Mind-Body Health Fits into Chronic Care  Gains of Using an App for Prediabetes
Gains of Using an App for Prediabetes  WHAT IS SLEEP APNEA AND WHY SHOULD YOU CARE?
WHAT IS SLEEP APNEA AND WHY SHOULD YOU CARE?  WHAT IS A VASECTOMY? EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW
WHAT IS A VASECTOMY? EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW  Teeth Whitening Newport Beach: What Results Can You Expect After One Session?
Teeth Whitening Newport Beach: What Results Can You Expect After One Session?  How to Choose the Best Products for Hyperpigmentation Based on Your Skin Type
How to Choose the Best Products for Hyperpigmentation Based on Your Skin Type